Products
-

1-Methoxy-2-propanol/CAS:107-98-2
Product Name:1-Methoxy-2-propanol
CAS:107-98-2
Type: ZA-Y
MF:C4H10O2
MW:90.12
STRUCTURE:
-

Steviol Glycosides / Stevioside /CAS:57817-89-7
Product name: Steviol Glycosides
Type:ZA-WW
CAS: 57817-89-7
MF:C38H60O18
MW: 804.88
-

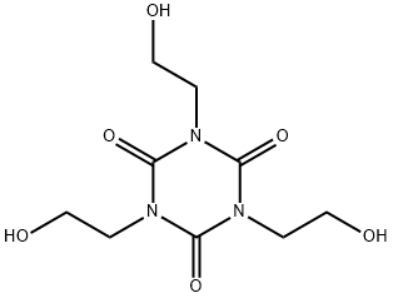
1,3,5-Tris(2-hydroxyethyl)cyanuric acid/CAS: 839-90-7
Product name:1,3,5-Tris(2-hydroxyethyl)cyanuric acid
Type:ZA-N
CAS: 839-90-7
MF:C9H15N3O6
MW: 261.23
STRUCTURE:
Density:1.498±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
Flash point: 241℃
White crystalline powder. Soluble in water and hot dilute alcohol, difficult to dissolve in ethanol, acetone, carbon tetrachloride, and petroleum ether.
-

Gallic acid/CAS: 149-91-7
Product name: Gallic acid
Type:ZA-N
CAS: 149-91-7
MF: C7H6O5
MW: 170.12
STRUCTURE:

Density: 1.694
Melting point: 251 °C (dec.) (lit.)
White or light brown needle-like crystals or powder. Melting point: 235-240℃ (decomposition). When heated to 100-120℃, it loses its crystalline water. When heated above 200℃, it loses carbon dioxide and forms pyrogallic acid (i.e., triphloroglucinol). It is soluble in hot water, ether, ethanol, acetone and glycerol, slightly soluble in cold water, and insoluble in benzene and chloroform.
-

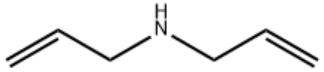
Diallylamine/CAS:124-02-7
Product Name: Diallylamine
Type: ZA-Y
CAS: 124-02-7
MF: C6H11N
MW: 97.16
STRUCTURE:
-

Dimethyl Sulfoxide/DMSO/CAS:67-68-5
Product Name: Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Type: ZA-Y
CAS:67-68-5
MF:C2H6OS
MW:78.13
STRUCTURE:

-

-

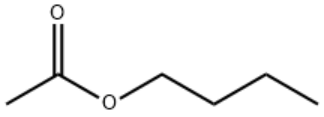
Butyl acetate/CAS:123-86-4
Product Name: Butyl acetate
Type:ZA-Y
CAS: 123-86-4
MF: C6H12O2
MW: 116.16
STRUCTURE:
-

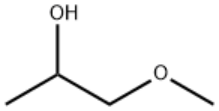
1-Methoxy-2-propanol/CAS:107-98-2
Product Name:1-Methoxy-2-propanol
Type: ZA-Y
CAS:107-98-2
MF:C4H10O2
MW:90.12
STRUCTURE:
-

Dibenzoylmethane / CAS120-46-7
Product name: Dibenzoylmethane
Type:ZA-N
CAS: 120-46-7
MF: C15H12O2
MW: 224.25
STRUCTURE:

Density: 0.800 g/cm3
Flash point: 219-221°C/18mm
Colorless rhombic plate-like crystals. Melting point 81℃, boiling point 219℃ (2.4kPa). It is readily soluble in chloroalcohol and chloroform, soluble in sodium hydroxide solution, insoluble in sodium carbonate solution, and slightly soluble in water.
-

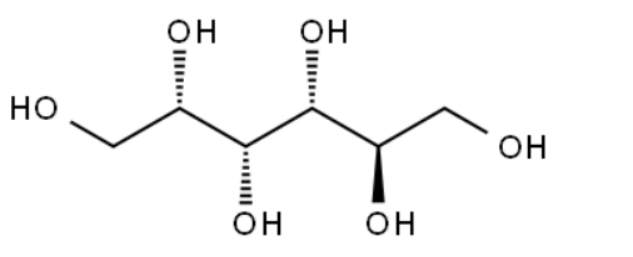
Sorbitol/CAS:50-70-4
Product Name:Sorbitol
Type:ZA-F
CAS:50-70-4
MF:C6H14O6
MW: 182.17
STRUCTURE:
-

Calcium hydroxide/CAS:1305-62-0
Product name: Calcium hydroxide
Type:ZA-N
CAS:1305-62-0
MF:CaH2O2
MW: 74.09
STRUCTURE:

Density: 2.24 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
melting point: 580 °C
chemical properties:
calcium hydroxide (calcium hydroxide), an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2, is commonly known as slaked lime or hydrated lime. It is a white powder-like solid. When water is added, it forms two layers. The upper layer of the aqueous solution is called clear lime water, and the lower layer of the suspension is called lime milk or lime slurry. The clear liquid on the upper layer, lime water, can be used to test for carbon dioxide, while the turbid liquid on the lower layer, lime milk, is a building material. The solubility of calcium hydroxide decreases with the increase of temperature. It is insoluble in alcohol but soluble in ammonium salts and glycerol. It can react with acids to form the corresponding calcium salts. At 580℃, it decomposes into calcium oxide and water.